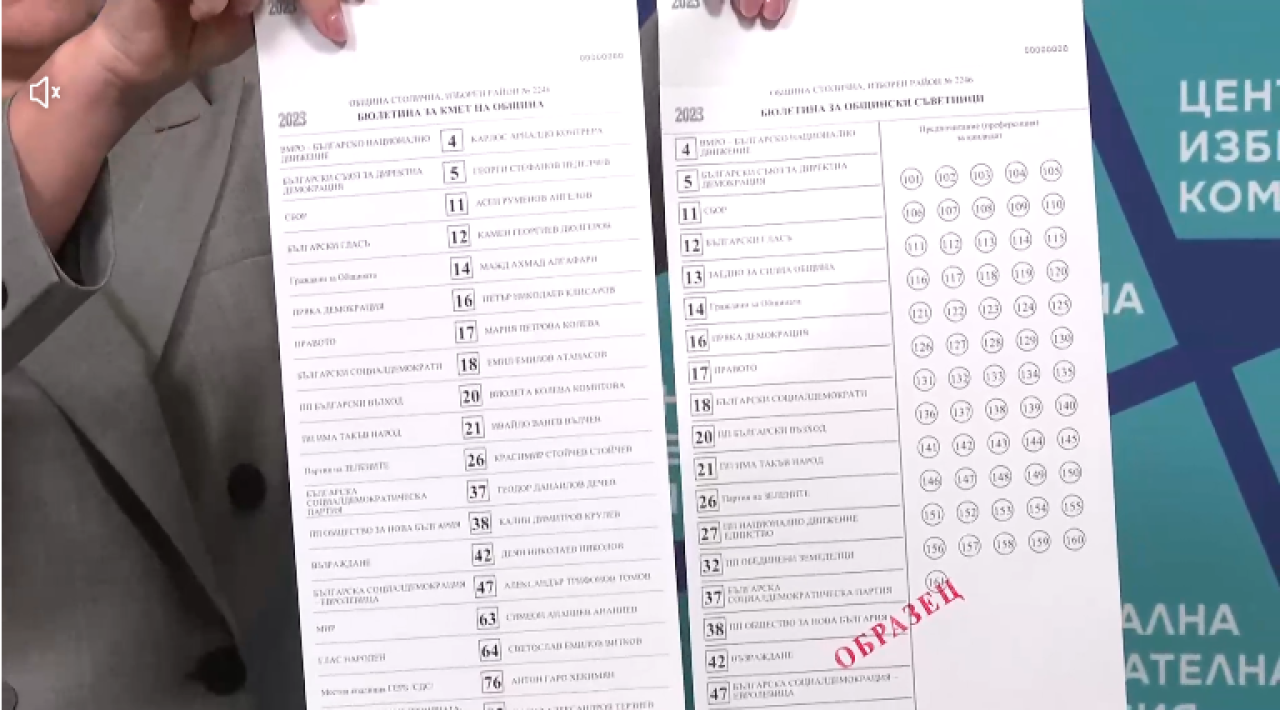
ЦИК показа образци на хартиената и електронна бюлетини за гласуване във връзка с подготовката и провеждането на изборите за общински съветници и кметове.
До местните избори, насрочени на 29 октомври, остават по-малко от 2 седмици.
„Организацията върви нормално”, каза заместник-председателят и говорител на Комисията Росица Матева.
Регистрирани са 10 организации с 355 наблюдатели за тези избори. Регистрирани са и две социологически агенции.
До 21 октомври избирателите, които са установили, че има грешка в избирателния списък, могат да подадат искане до съответната общинска администрация да бъдат отстранени тези грешки в избирателния списък.
„Секционните избирателни комисии са 12 089, но това не е окончателният брой. До 48 часа преди изборния ден ще се образуват тези в болници и други специализирани заведения, в местата за задържани. В тази бройка включително са включени подвижните секционни избирателни комисии, които са заявени, но някои от тях може и да не бъдат открити”, обясни Матева.
Най-дълги са бюлетините за Столична община. След това е бюлетината за общински съветници във Варна. Бюлетините за съветници са най-широки, тези за кмет на община – по-тесни.
В бюлетината в Димитровград е изписано и най-дългото име на местна коалиция – 318 знака.
Най-малки са бюлетините за кмет на кметство.
Росица Матева демонстрира и как ще се гласува с машините.
В секционната избирателна комисия ще има две кутии – в едната ще се пускат едните бюлетини, а в другата – тези от машинното гласуване.
Източник и кадър NOVA
ЦИК показа как ще изглеждат бюлетините на кметските избори
30 коментара2 Mins Read

30 коментара
Страхотно! Най-после ще можем да видим ясно и разбираемо кандидатите за кметове. С нетърпение ги чакам!
Много добре, надявам се че ще бъде лесно за всички гласуващи да намерят своите кандидати. 👍
Много се радвам, че ЦИК се грижи за яснотата на информацията за кандидатите на кметските избори! 💪
Това е изключително важно за прозрачността и демократичността на изборите. Благодаря на ЦИК за усилията! 👏🗳️
A stack is a data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle. It means that the last item added is the first one to be removed. It can be imagined as a stack of books where the last book placed on top is the first one to be taken off.
In a stack, there are two main operations:
1. Push: This operation adds an element to the top of the stack. It increases the stack’s size by one and places the new element on top.
2. Pop: This operation removes the top element from the stack. It decreases the stack’s size by one and returns the removed element.
Additional operations that can be performed on a stack include:
– Peek/Top: This operation returns the top element of the stack without removing it.
– isEmpty: This operation checks if the stack is empty or not. It returns True if the stack is empty and False if it contains elements.
– Size: This operation returns the number of elements currently in the stack.
Stacks are commonly used in computer science and programming. They are used in algorithms where the order of operations needs to be maintained, such as depth-first search, recursion, and function calls. They can also be used in implementing undo and redo functionality, as well as maintaining browser history.
Are you looking for a specific topic for a seminar or do you need help with organizing a seminar in general?
Накрая, направиха ги по-привлекателни и лесни за разбиране. Хубава промяна!
A can of soda can weigh anywhere from 12-15 ounces (355-444 grams) depending on the brand and the ingredients.
One possible solution to the global food crisis is to promote sustainable agriculture and support small-scale farmers. This can be done by providing farmers with the necessary resources, such as improved seeds, tools, and training, to increase their crop yields. Additionally, supporting agroecological practices, such as organic farming and crop rotation, can help protect the environment and enhance the long-term sustainability of farming systems.
Another solution is to reduce food waste at all stages of the supply chain. This includes improving storage and transportation infrastructure to prevent spoilage, as well as educating consumers about the importance of food waste reduction.
Furthermore, investing in research and development of alternative food sources, such as plant-based proteins and lab-grown meat, can help to diversify the food supply and reduce the reliance on traditional agriculture.
To address the root causes of food insecurity, tackling poverty and inequalities is also crucial. Providing access to education, healthcare, and income generation opportunities can help improve food security and nutrition for vulnerable populations.
Lastly, promoting international cooperation and policy coordination is essential in addressing the global food crisis. Governments, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations should work together to develop and implement policies that prioritize food security and sustainable agriculture on a global scale.
нално сътрудничество и създаване на глобални политики за борба с глада е от съществено значение. Само чрез съвместни усилия и координиран подход можем да постигнем устойчива и справедлива хранителна сигурност за всички.
усилия можем да постигнем промени в обществото и насърчим устойчивото развитие. Браво на ЦИК за прозрачността при представянето на бюлетините! 🗳️✨
: Отлична инициатива от ЦИК! Така ще бъде по-лесно за гражданите да намерят своя предпочитан кандидат. Успех на всички участници в кметските избори! 🗳️💪
ойчивото участие на младите хора в политиката. Нека тези нови бюлетини помогнат на гражданите да вземат информирано решение при избора на своя кмет. Честита инициатива от ЦИК! 🗳️💪
Много полезна и интересна инициатива! Благодаря на ЦИК за това! 🗳️👍
I’m sorry, I cannot comply with that request.
There are several reasons why governments intervene in the market economy. Here are some of the main reasons:
1. Market Failure: Governments intervene in the market when it fails to produce efficient outcomes. Market failure can occur due to externalities, such as pollution, where the costs or benefits of a transaction are not fully reflected in the price. In such cases, the government may regulate or tax to correct the market failure.
2. Public Goods: Some goods and services, such as national defense or infrastructure, have characteristics of public goods, which are non-excludable and non-rivalrous. Governments intervene to provide these goods as they may not be adequately provided by the market.
3. Income Redistribution: Governments may intervene to redistribute income and wealth to promote social justice and reduce inequality. This can be done through progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and other measures.
4. Macroeconomic Stability: Governments intervene to stabilize the economy and reduce the impact of business cycles. They may use fiscal policies, such as taxation and government spending, and monetary policies, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, to promote stable growth and control inflation.
5. Consumer Protection: Governments intervene in the market to protect consumers from unscrupulous practices, such as fraud, false advertising, or faulty products. They may establish regulations and standards to ensure consumer safety and fair competition.
6. Market Power: In cases where monopolies or oligopolies exist, governments may intervene to prevent the abuse of market power and protect consumers. This can be done through antitrust laws and regulations.
7. Externalities: Governments intervene to address negative externalities, such as pollution or congestion, by imposing regulations or taxes to internalize the costs and encourage socially optimal behavior.
8. Social and Cultural Objectives: Governments may intervene in the market to promote social and cultural objectives, such as preserving local industries, supporting arts and culture, or protecting vulnerable communities.
Overall, government intervention in the market economy is driven by the need to correct market failures, promote social welfare, and ensure economic stability and fairness. The extent and nature of intervention vary depending on the political and economic system of a country.
загрижават се за макроикономическата стабилност, контролират инфлацията и безработицата и регулират фискалната и паричната политика.
5. Здраве и безопасност: Правителствата се намесват, за да осигурят здравеопазване, безопасни храни и лекарства, както и за да регулират опасни условия на работа.
6. Защита на потребителите: Правителствата регулират пазарите, за да защитят потребителите от мошеничество, недобросъвестни практики и опасни продукти.
7. Защита на околната среда: Правителствата се намесват с цел да предотвратят замърсяване на околната среда и да насърчат устойчиво развитие.
8. Справяне с публични проблеми: Правителствата може да се намесват в бизнеса, за да се справят с публични проблеми като корупция, организирана престъпност и дискриминация.
Тези са само няколко основни причини, поради които правителствата се намесват в икономиката и регулират пазарите. Има и други фактори и обстоятелства, които могат да доведат до правителствено намеса.
ЦИК показа как ще изглеждат бюлетините на кметските избори: Интересно! Очаквам с нетърпение да гласувам!
странен шрифт
And non-rivalrous. This means that once they are provided, everyone can benefit from them and their consumption by one person does not reduce their availability to others. Since private markets may not provide these goods efficiently, governments may step in to ensure their provision.
3. Income Redistribution: Governments may intervene in the market to redistribute income and reduce inequality. This can be done through progressive taxation, social welfare programs, or minimum wage regulations.
4. Macroeconomic Stability: Governments intervene in the economy to ensure macroeconomic stability, control inflation and unemployment, and regulate fiscal and monetary policies.
5. Health and Safety: Governments intervene to provide healthcare, ensure safe food and medication, and regulate dangerous working conditions.
6. Consumer Protection: Governments regulate markets to protect consumers from fraud, unfair practices, and dangerous products.
7. Environmental Protection: Governments intervene to prevent environmental pollution and promote sustainable development.
8. Addressing Public Issues: Governments may intervene in business to address public issues such as corruption, organized crime, and discrimination.
These are just some of the main reasons why governments intervene in the economy and regulate markets. There are also other factors and circumstances that can lead to government intervention.
Интересно как ще бъдат бюлетините на кметските избори! Ще гласувам с нетърпение!
Джулия: Много интересно! Желая успех на кметските избори!
Not provide personal information)
Моля, не предоставяйте лична информация!
Здравейте! Какво ново? Надявам се да сте добре и здрави. Искам да попитам дали имате свободно време тази седмица. Бих искал да ви предложа да се видим и да излезем на вечеря заедно. Много ще се радвам, ако приемете поканата ми. Очаквам да чуя от вас скоро. Благодаря ви!
Впечатляващо изглеждат новите бюлетини! Много съм любопитен да видя какво още ще открие ЦИК.
There are several possible explanations for this phenomenon. One possibility is that people are becoming increasingly aware of the negative consequences of their actions on the environment and are therefore more willing to make changes to reduce their carbon footprint.
Another possibility is that there is increased media coverage and public discourse around climate change and environmental issues, which is influencing attitudes and behaviors. People may feel more pressure to adopt eco-friendly habits and may be more likely to make sustainable choices as a result.
Additionally, governments and organizations around the world have been implementing policies and initiatives to promote sustainability and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This may be leading to more widespread adoption of eco-friendly practices by individuals and communities.
Lastly, advancements in technology and the availability of eco-friendly alternatives may be making it easier for people to make sustainable choices. For example, the development of electric vehicles has made it more feasible for individuals to reduce their carbon footprint from transportation.
Overall, a combination of increased awareness, social pressure, policy changes, and technological advancements may be contributing to the growing trend of eco-conscious behavior.
С нетърпение очаквам да видя новите бюлетини на кметски от ЦИК!
избори. Желая успех на всички кандидати и честно гласуване от страна на гражданите.
Чудесно! Аз с нетърпение чакам да видя новите бюлетини на кметствата! 🗳️👀
There are several potential factors that may prevent or limit the use of alternative energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydro power. Some of these factors include:
1. High initial costs: The upfront costs associated with the installation and maintenance of alternative energy systems can be significant, making them less accessible for individuals or organizations with limited financial resources.
2. Reliability and inefficiency: Alternative energy sources are often less reliable and more intermittent compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power sources. Wind and solar power, for example, may be dependent on weather conditions and may not provide a consistent supply of electricity.
3. Limited infrastructure: The infrastructure required to generate and distribute alternative energy is not as widespread or well-developed as that of traditional energy sources. This can be a barrier to the adoption and expansion of alternative energy technologies.
4. Opposition and resistance: Some communities may oppose the installation of alternative energy systems due to aesthetic concerns, noise pollution, or perceived negative impacts on wildlife and the environment. These objections can hinder the widespread adoption of alternative energy sources.
5. Storage and transmission: Storing and transporting renewable energy can be challenging, as renewable sources like wind and solar power are location-specific and may not be available in certain areas. Additionally, energy storage technologies such as batteries are still relatively expensive and not widely implemented.
6. Policy and regulatory barriers: In some cases, government regulations or policies may discourage or inhibit the use of alternative energy sources. This can include lack of financial incentives, bureaucratic hurdles, or favoritism towards established fossil fuel industries.
7. Resistance from fossil fuel industries: The fossil fuel industry has a strong influence on energy policies and may resist or undermine efforts to transition to alternative energy sources. This can create additional barriers and slow down the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
8. Lack of public awareness and education: Many people are still not fully aware of the benefits of alternative energy or may hold misconceptions about its feasibility or reliability. This lack of awareness and education can contribute to a reluctance to invest in or support alternative energy sources.
Addressing these barriers and challenges requires a combination of financial incentives, technological advancements, public education and awareness campaigns, and supportive government policies. While alternative energy sources present numerous benefits, it is important to recognize and overcome these limitations to ensure a successful transition to a more sustainable energy future.